



The mechanisms of Taxifolin action in the cardiovascular system are mainly associated with antioxidant effects, alterations in NO production by endothelial (eNOS) and inducible NOS (iNOS), anti-inflammatory action, and modulation of the RAS and/or SNS. Another important role of Taxifolin concerns the rheological properties of blood and deformability of red blood cells.
Furthermore, the improvement in vascular function caused by Taxifolin accounts for particularly important effects, as the prevention and treatment of endothelial dysfunction contribute to the improvement of blood flow and oxygenation of all tissues.
It is well known that the rheological properties of blood are directly involved in the regulation of blood pressure and hypertension development [175,176].
Taxifolin inhibits platelet aggregation induced by ADP and thrombin release [95]. Kubatiev et al. showed that Taxifolin causes a concentration-dependent decrease in cytoplasmic Ca2+ levels in thrombocytes induced by ADP or thrombin probably via the Ca2+ inhibition channels [94]. Higher concentrations of Taxifolin decreased the basal cytoplasmatic Ca2+ concentration probably due to the elevation in the cAMP level. Similar inhibition of ADP-induced thrombocyte aggregation by Taxifolin was reported by [96]. Furthermore, Taxifolin provided protection against hemolysis induced by free radicals as well as against nonoxidative hemolytic enzyme phospholipase C [96].
These studies showed that Taxifolin may provide protection against red blood cell aggregation, coagulation, and thrombogenesis and that they can elevate red blood cell deformability, which can be another beneficial effect for subjects suffering from hypertension and/or COVID-19.
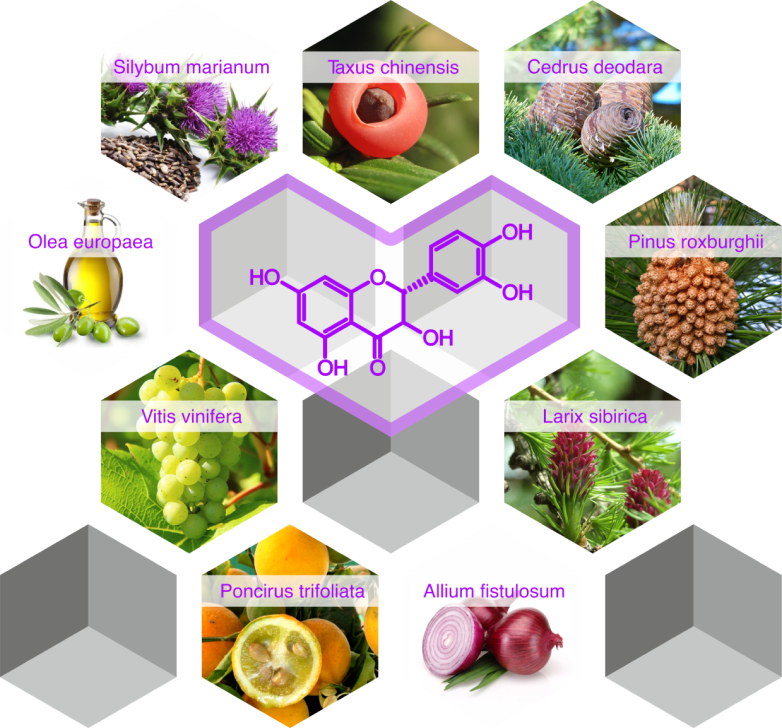
Dihydroquercetin extracted from the root part of Siberian larch by a unique technology, preserving its natural structure and healing properties, has the greatest degree of the necessary effect and is the reference antioxidant. High-purity dihydroquercetin (Taxifolin) (above 98% purity) exceeds other known antioxidants by almost 11 times in potency.
References: Iveta Bernatova , Silvia Liskova. Review Mechanisms Modified by Epicatechin and Taxifolin Relevant for the Treatment of Hypertension and Viral Infection: Knowledge from Preclinical Studies. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030467